How is the global climate?
One of the most important factors affecting regional climate is the solar radiation, known as insolation, received. A simple climate classification divides the Earth into climatic zones by the Arctic Circle, the Tropic of Cancer, the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle. Tropical zone refers to the region between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn; temperate zone refers to the region between the Arctic Circle (the Antarctic Circle) and the Tropic of Cancer (the Tropic of Capricorn); polar zone fills the areas within the Arctic and Antarctic Circles. Among the three climatic zones, tropical zone receives the greatest amount of insolation, and polar zones receive the least.
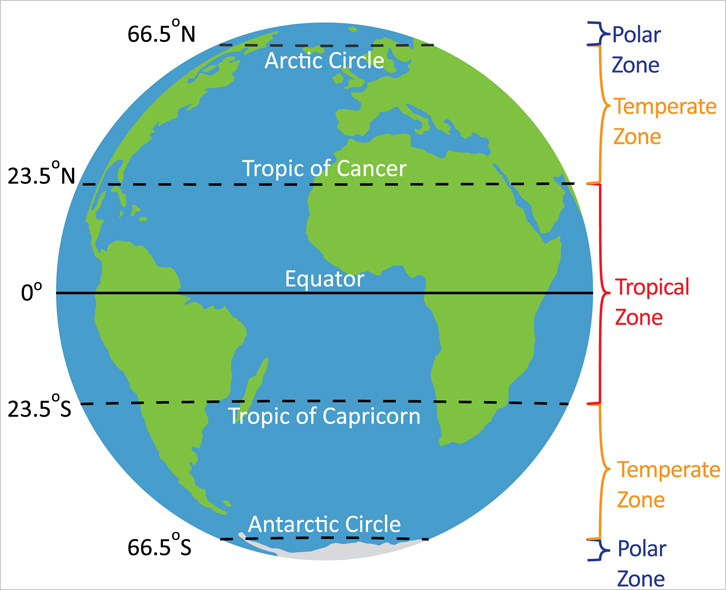 |
|
| Fig 1.2 Climatic zones classified by the Tropic of Capricorn, the Tropic of Cancer, the Antarctic Circle and the Arctic Circle |
Other climate classifications may take into account parameters such as temperature, precipitation, duration of precipitation and types of vegetation. Regions with similar parameters will be grouped into a climatic zone. For example, Köppen’s climatic classification divides the world into 6 major climatic zones based on 3 factors: growth of vegetation, temperature and precipitation.
In addition to latitude, there are other factors such as geographical location, altitude, distance from the sea, ocean currents and prevailing wind, which affect the regional climate.
★ More information
Climatic zones (Köppen climatic classification)
www.metoffice.gov.uk/climate-guide/climate/zones

