Greenhouse gases
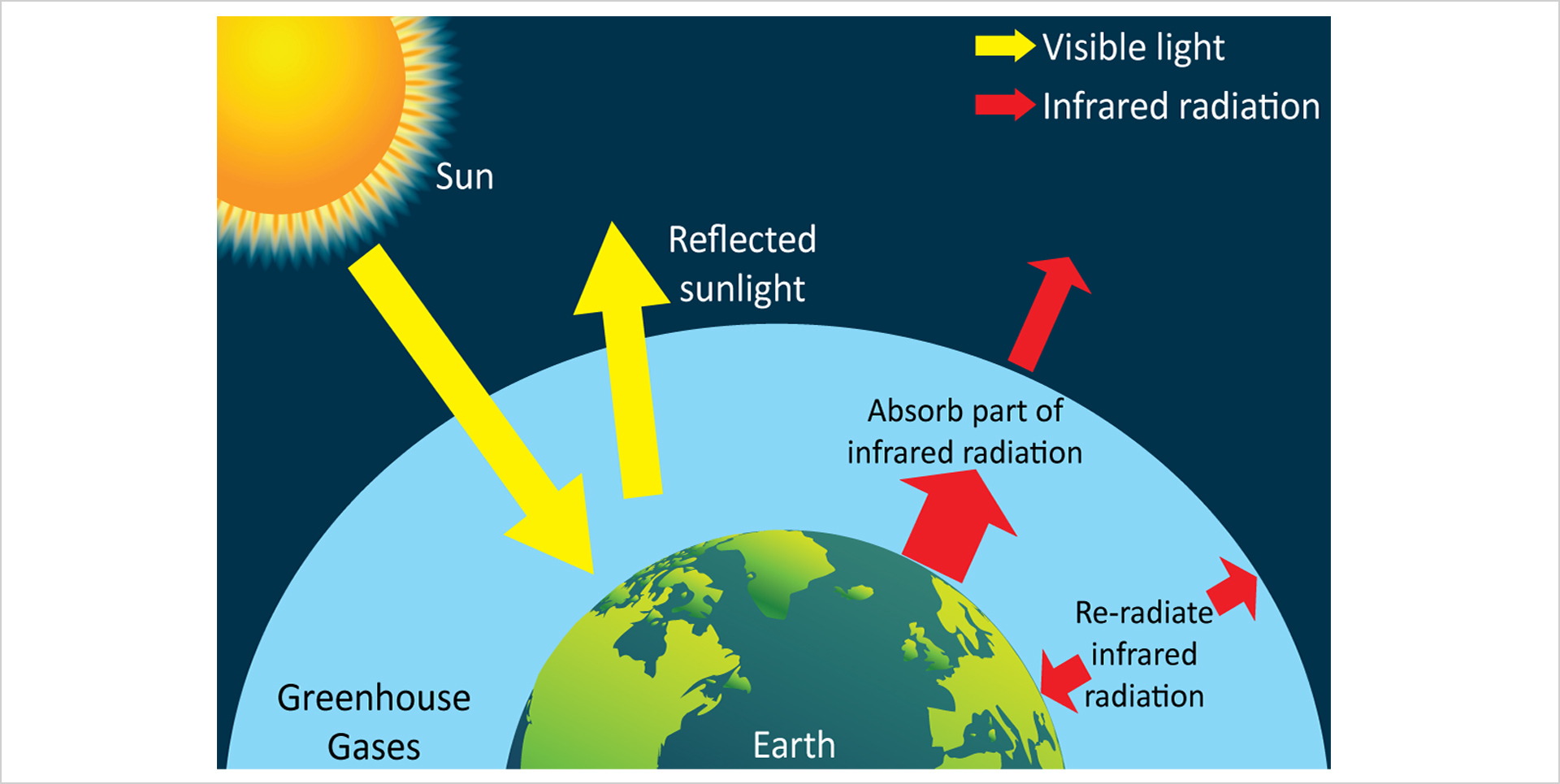
Greenhouse effect
Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide occur naturally in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases absorb part of the infrared radiation emitted from the Earth and then re-radiate the energy in all directions, also in the form of infrared radiation. Part of the infrared radiation goes back to the Earth, heating up the surface. This is known as the greenhouse effect.
Fig2.7 Greenhouse effect
Carbon cycle
Carbon cycle is a biogeochemical cycle in which carbon is continuously exchanged and recycled among several natural reservoirs, including atmosphere, ocean, biosphere, rocks and fossil fuels, where carbon is stored.
In an unperturbed natural carbon cycle, these exchanges between reservoirs are approximately balanced.
★ More information
Carbon cycle
https://www.hko.gov.hk/climate_change/ele-carboncycle_d3_e.htm
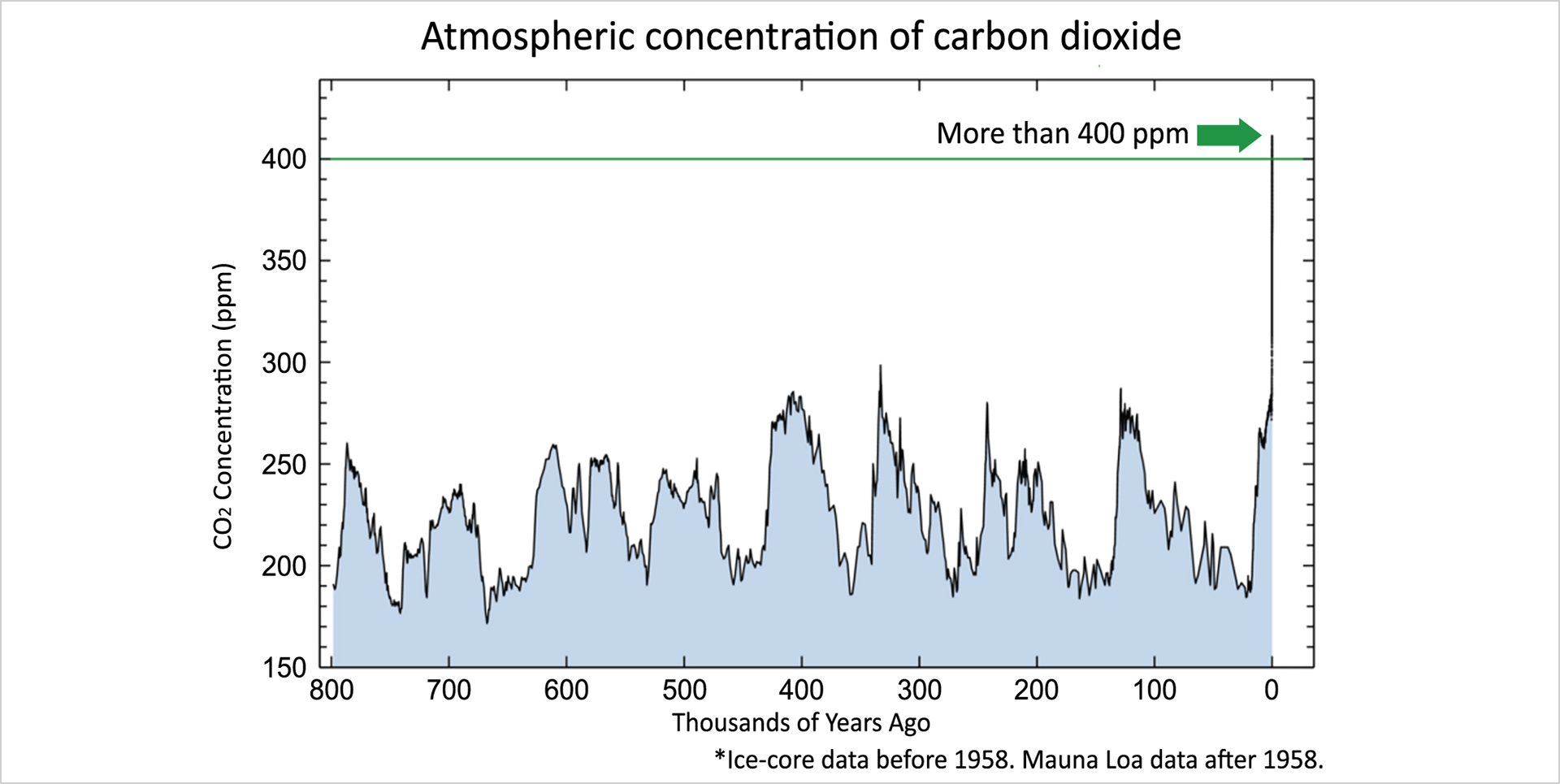
In the last 800,000 years before the Industrial Revolution, the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide fluctuated roughly between 180 and 280 ppm1 . However, human activities have disturbed the global carbon cycle. The present-day atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide has exceeded 400 ppm, unprecedented in the past 800,000 years. And the concentration keeps on rising.

[1] ppm stands for “parts per million”
Fig2.8 Atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide vii (Source: Scripps Institution of Oceanography)
★ More information
Global carbon dioxide concentration
www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/global.html
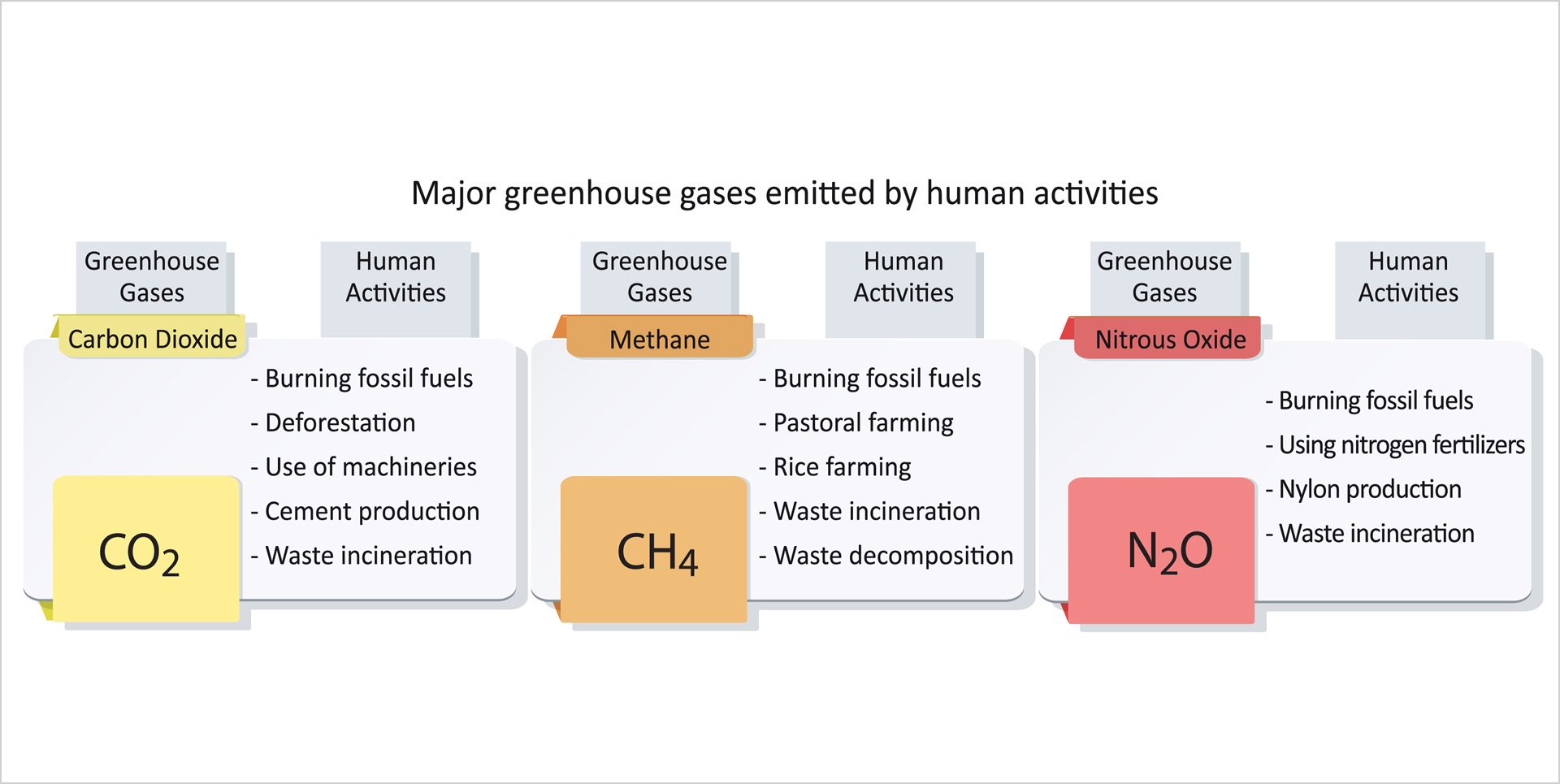
What human activities increase greenhouse gases
Human activites emit huge amount of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, enhancing the greenhouse effect to trap more energy on Earth and leading to global warming.

Table 2.1 Major greenhouse gases emitted by human activities
★ More information
History of atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide
www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/history.html
Animation of atmospheric carbon dioxide
(a)Burning fossil fuels
Fossil fuels include coal, oil and natural gas. Humans have been burning massive amount of fossil fuels for many purposes since the Industrial Revolution, such as power generation, heating and powering machines and vehicles. Large amounts of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide are emitted to the atmosphere.
(b)Deforestation
To acquire land for agricultural and urban development, forests are cut down or burned on a massive scale. Carbon dioxide is released from the burning process. Moreover, plants capable of absorbing and storing carbon dioxide decrease, resulting in increasing atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide. Dataviii show that around 140 million hectares of forest are lost globally for 1990-2015.
(c)Agricultural activities
Pastoral farming emits a lot of methane, e.g. cows ruminating, and so does rice farming. The use of large amounts of nitrogen fertilizers releases nitrous oxide. Moreover, agricultural machineries are mostly powered by fossil fuels and therefore contribute to carbon dioxide emission.
(d)Industrial activities
Industrial activities emit large amount of greenhouse gases. For example, the production of nylon releases nitrous oxide and the production of cement releases carbon dioxide. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which were developed and used as refrigerants and aerosol propellants in the past century, are also greenhouse gases.
★ More information
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
www.ncdc.noaa.gov/monitoring-references/faq/greenhouse-gases.php?section=cfc
(e)Waste treatment
With improving living standard and the rise of consumerism, humans consume resources and produce large amounts of waste as well. Wastes are treated by either incineration or landfilling. The incineration process produces carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide while waste decomposition in landfills produces methane.
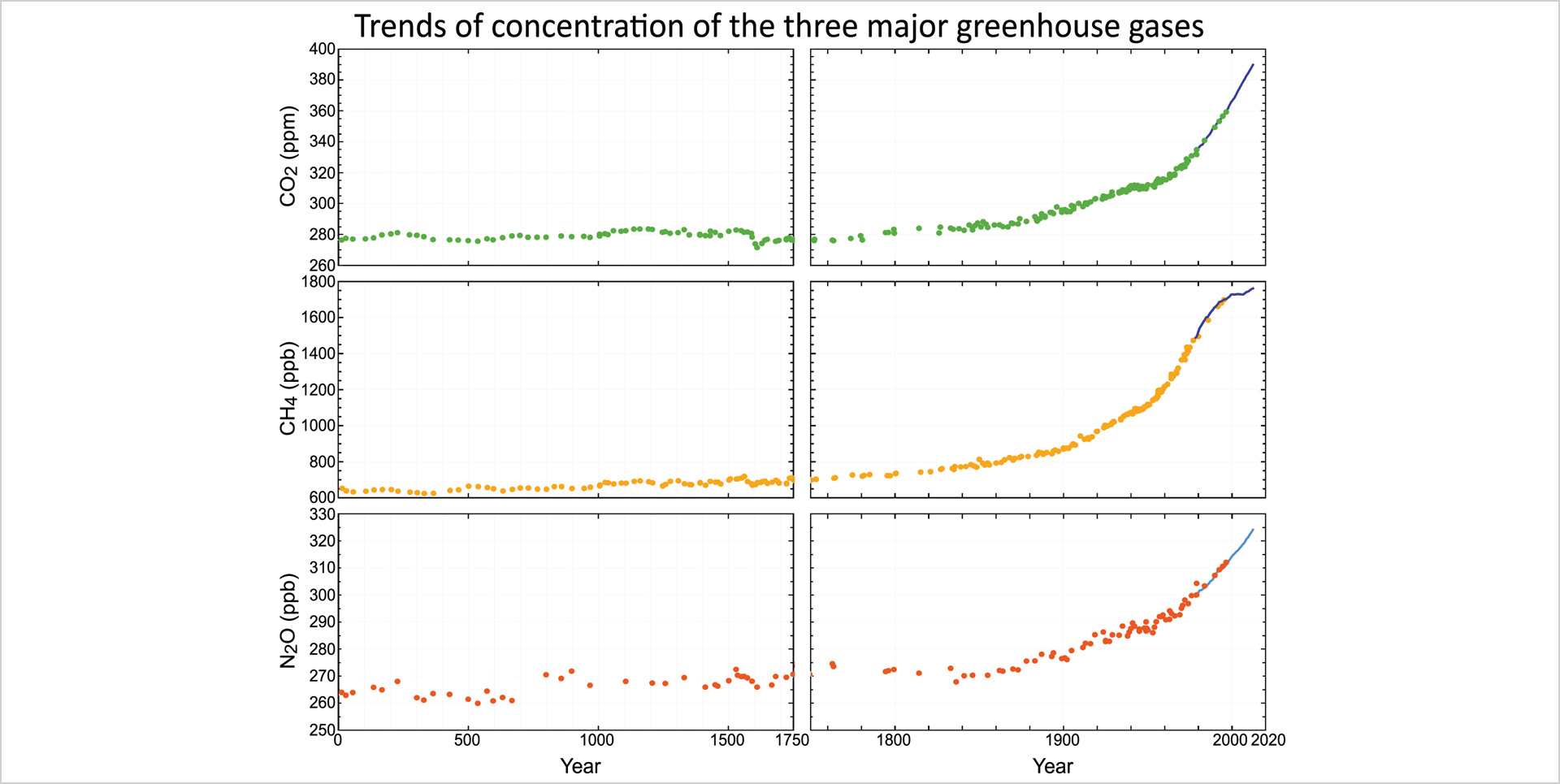
Since 1750, the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide has increased by more than 40%. Methane and nitrous oxide have increased by about 160% and 20% respectively.
➤ Do volcanoes emit more carbon dioxide than human activities?
One of the natural factors affecting the climate is volcanic eruptions, in which carbon dioxide is released to the atmosphere. However, as indicated by various studies, in the past century, the annual amount of carbon dioxide released by human activities far exceeded the total amount released by terrestrial and submarine volcanoes. Latest data shows that human activities emit 60 times or more the amount of carbon dioxide released by volcanoes each year.
Fig 2.9 Trends of concentration of the three major greenhouse gases ix (Source: The Fifth Assessment Report of IPCC)
Note: ppm and ppb stand for “parts per million” and “parts per billion” respectively
★ More information
The latest global CO2 concentration
www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/global.html
WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin
https://public.wmo.int/en/resources/library/wmo-greenhouse-gas-bulletin